Python Data Structures —— Basic
13 Aug 2014 Python Data Structure本文主要总结Python内置数据结构的性能分析和基本线性结构的Python实现。
Python内置数据结构的性能分析
-
Big-O Efficiency of Python List Operators

-
Big-O Efficiency of Python Dictionary Operators

Linear Structures
Stack 栈
LIFO, last-in first-out 栈可以解决若干问题,如检查括号匹配、进制间转换、逆波兰表达式求值、图的深度搜索等。 Stack ADT:
Statck()creates a new stack that is empty.push(item)adds a new item.pop()removes the top item.peek()returns the top item from the stack but does not remove it.isEmpty()tests to see whether the stack is empty.size()returns the number of item on the stack.
Stack Implement:
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
return self.items.pop()
def peek(self):
return self.items[len(self.items)-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
Queue 队列
FIFO, first-in first-out 队列一般用于解决需要优先队列的问题或者进行广度优先搜索的问题等。 Queue ADT:
Queue()creates a new queue that is empty.enqueue(item)adds a new item to the rear of the queue.dequeue()removes the front item from the queue.isEmpty()tests to see whether the queue is empty.size()returns the number of item in the queue .
Queue Implement:
# 假设list中index为0的位置为尾部
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.items.insert(0, item)
def dequeue(self):
return self.items.pop()
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
# 也可直接使用deque库实现队列的插入删除
from collections import deque
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.items = deque([])
def enqueue(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
return self.items.popleft()
Deque (Double-Queue) 双向队列
 双向队列是头尾都可以进行插入和删除的队列。可用于解决回文检查问题。
Deque ADT:
双向队列是头尾都可以进行插入和删除的队列。可用于解决回文检查问题。
Deque ADT:
Deque()creates a new deque that is empty.addFront(item)adds a new item to the front of the deque.addRear(item)adds a new item to the rear of the deque.removeFront()removes the front item from the deque.removeRear()removes the rear item from the deque.isEmpty()tests to see whether the deque is empty.size()returns the number of items in the deque.
Deque Implement:
# 假设list中index为0的位置为尾部
class Deque:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def addFront(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def addRear(self, item):
self.items.insert(0, item)
def removeFront(self):
return self.items.pop()
def removeRear(self):
return self.items.pop(0)
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
# 也可直接使用deque库实现队列的插入删除
from collections import deque
addFront: appendleft(x)
addRear: append(x)
removeFront: popleft()
removeRear: pop()
Linked List(Unordered) 链表
Linked List ADT:
List()creates a new list that is empty.add(item)adds a new item to the list head.remove(item)removes the item from the list.search(item)searches for the item in the list.isEmpty()tests to see whether the list is empty.size()returns the number of items in the list.append(item)adds a new item to the end of the list making it the last item in the collection.index(item)returns the position of item in the list.insert(pos,item)adds a new item to the list at position pos.pop()removes and returns the last item in the list.pop(pos)removes and returns the item at position pos.
在头部插入:
 在头部删除:
在头部删除:
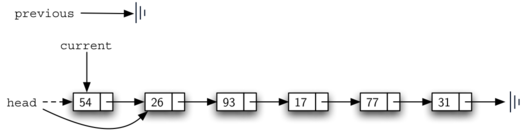 在中间删除:
在中间删除:
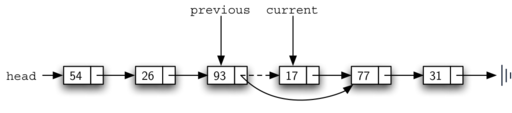
Linked List Implement:
class Node:
def __init__(self, initdata):
self.data = initiate
self.next = None
def getData(self):
return self.data
def getNext(self):
return self.next
def setData(self, newdata):
self.data = newdata
def setNext(self, newnext):
self.next = newnext
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def isEmpty(self):
return self.head == None
def add(self, item):
temp = Node(item)
temp.setNext(self.head)
self.head = temp
def size(self):
current = self.head
count = 0
while current != None:
count = count + 1
current = current.getNext()
return count
def search(self, item):
current = self.head
found = False
while current != None and not found:
if current.getData() == item:
found = True
else:
current = current.getNext()
return found
def remove(self, item):
current = self.head
previous = None
found = False
while not found:
if current.getData() == item:
found = True
else:
previous = current
current = current.getNext()
if previous == None:
self.head = current.getNext()
else:
previous.setNext(current.getNext())
Reference:《Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures Using Python》。