二叉树的遍历
12 Jun 2016 Algorithm Leetcode二叉树的遍历是按照某条搜索路径依次访问树中的每一个结点,使得每个结点有且仅被访问一次。常见的遍历次序有:
- 先序遍历:先访问根结点,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树
- 中序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问根结点,最后访问右子树
- 后序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根结点
二叉树遍历的实现方式有三种,分别为:递归遍历、非递归遍历和Morris遍历。
二叉树结点的定义如下:
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
递归遍历
递归实现非常简单,按照遍历的次序,对当前结点分别调用左子树和右子树即可。二叉树遍历的递归实现,每个结点只需遍历一次,时间复杂度为O(n)。因为使用了递归,最差情况下递归调用的深度为O(n),所以空间复杂度为O(n)。
# preorder:root->left->right
def preorder(tree):
if tree:
print tree.val
preorder(tree.left)
preorder(tree.right)
# inorder: left->root->right
def inorder(tree):
if tree:
inorder(tree.left)
print tree.val
inorder(tree.right)
# postorder: left->right->root
def postorder(tree):
if tree:
postorder(tree.left)
postorder(tree.right)
print tree.val
非递归遍历
非递归实现借助栈。二叉树遍历的非递归实现,每个结点只需遍历一次,时间复杂度为O(n)。因为使用了栈,空间复杂度为二叉树的高度,故空间复杂度为O(n)。
# preorder
def preorderTraversal(root):
result, stack = [], []
current = root
while stack or current:
if current:
result.append(current.val)
stack.append(current)
current = current.left
else:
current = stack.pop()
current = current.right
return result
# inorder
def inorder(root):
result, stack = [], []
current = root
while stack or current:
if current:
stack.apend(current)
current = current.left
else: # not have left
current = stack.pop()
result.append(current.val)
current = current.right
return result
# postorder
def postorder(root):
result, stack = [], []
current, last = root, None
while stack or current:
if current:
stack.append(current)
current = current.left
else:
parent = stack[-1]
if parent.right in (None, last):
result.append(parent.val)
last = stack.pop()
else:
current = parent.right
return result
Morris遍历
Morris遍历算法只需要常数空间O(1)即可,在O(n)时间内完成二叉树的遍历。要使用O(1)空间进行遍历的困难之处在于遍历到子结点的时候如何重新返回到父节点?为了解决这个问题,Morris遍历方法用到了线索二叉树。它的原理很简单,只需要利用叶子节点中的左右空指针指向某种顺序遍历下的前驱节点或后继节点即可。
使用二叉树中的叶节点的右指针来保存后面将要访问的节点的信息,当这个右指针使用完成后,再将它置为None。在访问过程中有些节点会访问两次,所以与递归的空间换时间的思路不同,Morris是使用时间换空间的思想。
中序遍历步骤:
- 如果当前节点的左孩子为空,则输出当前节点并将其右孩子作为当前节点。
- 如果当前节点的左孩子不为空,在当前节点的左子树中找到当前节点在中序遍历下的前驱节点。 a) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为空,将它的右孩子设置为当前节点。当前节点更新为当前节点的左孩子。 b) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为当前节点,将它的右孩子重新设为空(恢复树的形状)。输出当前节点。当前节点更新为当前节点的右孩子。
- 重复以上1、2直到当前节点为空。
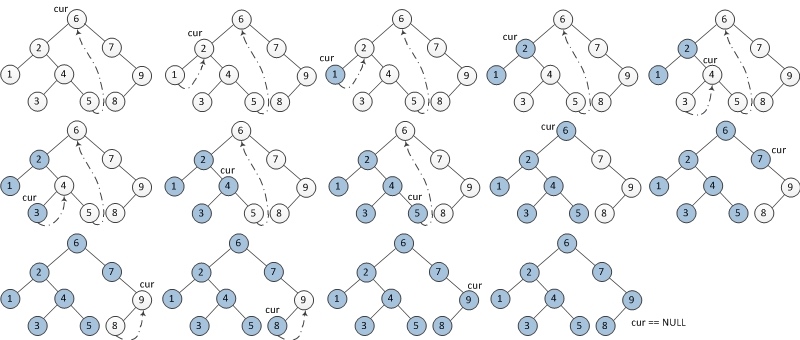 

前序遍历步骤:
- 如果当前节点的左孩子为空,则输出当前节点并将其右孩子作为当前节点。
- 如果当前节点的左孩子不为空,在当前节点的左子树中找到当前节点在中序遍历下的前驱节点。 a) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为空,将它的右孩子设置为当前节点。输出当前节点(在这里输出,这是与中序遍历唯一一点不同)。当前节点更新为当前节点的左孩子。 b) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为当前节点,将它的右孩子重新设为空。当前节点更新为当前节点的右孩子。
- 重复以上1、2直到当前节点为空。
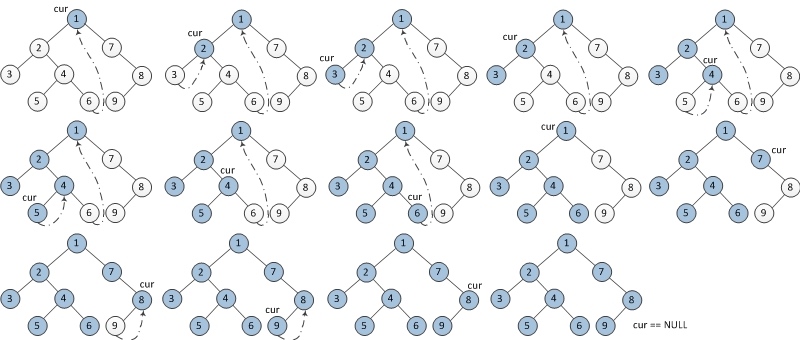 

后序遍历步骤:
- 建立一个临时节点dump,令其左孩子是root, 将临时节点dump设置为当前节点。
- 如果当前节点的左孩子为空,则将其右孩子作为当前节点。
- 如果当前节点的左孩子不为空,在当前节点的左子树中找到当前节点在中序遍历下的前驱节点。 a) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为空,将它的右孩子设置为当前节点。当前节点更新为当前节点的左孩子。 b) 如果前驱节点的右孩子为当前节点,将它的右孩子重新设为空。倒序输出从当前节点的左孩子到该前驱节点这条路径上的所有节点。当前节点更新为当前节点的右孩子。
- 重复以上2、3直到当前节点为空。
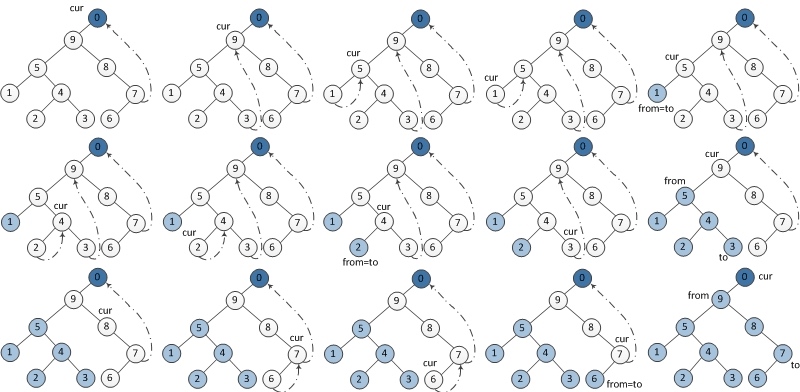 

# preorder
def inorder(root):
result = []
prev, cur = None, root
while cur:
if cur.left is None:
result.append(cur.val)
prev = cur
cur = cur.right
else:
node = cur.left
while node.right and node.right != cur:
node = node.right
if node.right is None:
result.append(cur.val)
node.right = cur
prev = cur
cur = cur.left
else:
node.right = None
prev = cur
cur = cur.right
return result
# inorder
def inorder(root):
result = []
prev, cur = None, root
while cur:
if cur.left is None:
result.append(cur.val)
prev = cur
cur = cur.right
else:
node = cur.left
while node.right and node.right != cur:
node = node.right
if node.right is None:
node.right = cur
cur = cur.left
else:
result.append(cur.val)
node.right = None
prev = cur
cur = cur.right
return result
# postorder
def postorder(root):
dummy = TreeNode(0)
dummy.left = root
result, cur = [], dummy
while cur:
if cur.left is None:
cur = cur.right
else:
node = cur.left
while node.right and node.right != cur:
node = node.right
if node.right is None:
node.right = cur
cur = cur.left
else:
result += traceBack(cur.left, node)
node.right = None
cur = cur.right
def traceBack(fromNode, toNode):
result, cur = [], fromNode:
while cur is not toNode:
result.append(cur.val)
cur = cur.right
result.apend(toNode.val)
reuslt.reverse()
return result
Reference :
[1] Morris二叉树遍历算法
[2] Morris Traversal方法遍历二叉树
[3] Leetcode: 94, 144, 145